It’s been said that modern life is made of ABS plastic. Whether or not it’s true, its light weight and ability to easily be mass-produced have made it indispensable for industrial products. Today, 8 million tons of ABS are produced worldwide each year.
Let’s explore this versatile material and the features that make it so popular.
What is ABS material?
ABS is the ISO abbreviation for acrylonitrile (AN), butadiene (BD) and styrene (ST) — a polymer alloy (i.e., polymeric multi-component plastics that includes copolymerization).
When using the ABS acronym there can be some confusion whether you’re referring to a final product or raw material. As a rule of thumb, ABS is a general reference to material and final products while ABS resin is the unprocessed, raw form used in manufacturing.
ABS resin can be manufactured in two ways:
- Polymer blending: Butadiene (BD) and additives are combined with AS resin acrylonitrile (AN) and styrene (ST) — mixed and transformed into pellets using an extruder
- Emulsion grafting: Styrene (ST) is mixed with acrylonitrile (AN), latex, emulsifiers and more; the moisture is removed using a centrifuge and then converted to pellets in an extruder
Once molded, ABS has incredible aesthetic advantages. Its naturally smooth and glossy finish can easily be texturized as needed. Additionally, it maintains vibrant color, making it suitable for printing, painting and other decoration.
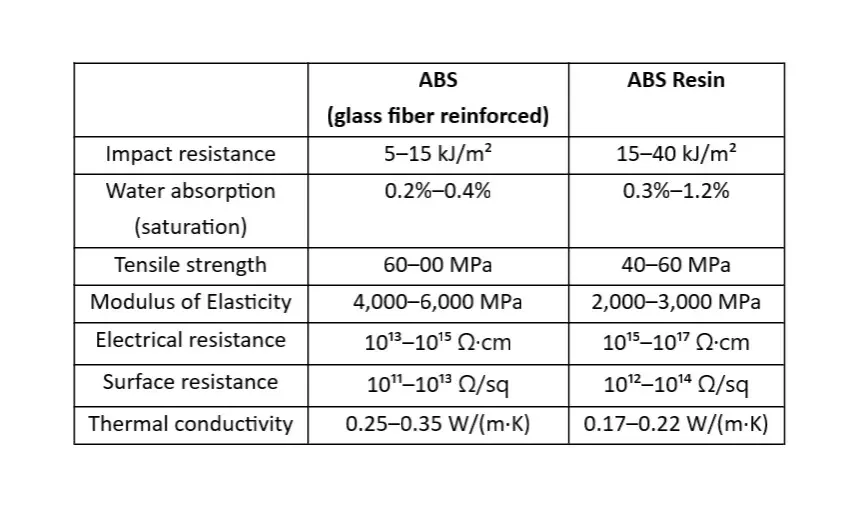
ABS plastic properties and ABS resin properties
As we’ve noted, ABS and ABS plastic resin refer to the same material but in different stages of the production process. In its raw form, it is possible to create a material that meets the required performance by adjusting the ratio of each component (AN, BD or ST). For example, increasing AN enhances strength and elastic modulus, while increasing ST elevates fluidity and increasing BD boosts impact resistance.
However, when comparing the properties, there may be differences between ABS resin and completed ABS products with additives. For example, the typical ABS density range for the raw resin or unreinforced finished products is 1.04-1.10 g/cm³; however, something like glass fibers change those figures. Additional figures include*:
*Plastics: Thermoplastics, Thermosets, and Elastomers", Handbook of Materials Selection,
Edward N. Peters.
Is acrylonitrile butadiene styrene toxic?
The short answer is no. ABS plastics are non-toxic in their solid and finished form. They’re frequently found in non-food items like consumer electronics, automotive parts and toys.
Safety concerns come into consideration when ABS is heated during the manufacturing process. Although ABS heat resistance is high when finished, it is soft during processing for moldability. While soft, it can potentially release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and styrene fumes, which have long-term health effects. Additionally, if ABS burns, it emits toxic gases like hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide. To avoid exposure to harmful fumes, it’s recommended that ABS is manufactured in well-ventilated areas and proper fire safety measures are taken.
Is ABS recyclable?
Since ABS is a thermoplastic (i.e., it can be melted and reshaped without a major decline in its properties), it is recyclable. The process includes collecting products, cleaning, shredding, melting and reforming them into pellets to create new items.
The repurposing process can be labor intensive, as many products include additives like coatings or adhesives that must be separated from the product before beginning. Because of this, specialized sorting equipment may be needed—something not all recycling facilities are equipped with. It’s recommended that you research locations near you that can handle ABS.
ABS: Durable and attractive
ABS is a multi-purpose material that blends strength, resilience and aesthetics. Through research and development, it continues to prove itself as a timeless material that meets modern needs and paves the way for advancement.