Have you ever looked at something plastic and wondered, "How in the world is this made?" Moldable plastic materials are everywhere, from small cosmetic bottles to large playground equipment. The question is: Which plastics can be molded with heat?
Let's take a look.
Choosing a moldable plastic
There are two types of moldable plastic materials, and your final product will determine which you choose. Start by considering the product’s complexity and size, then ask:
Once you’ve answered these, look at the two available materials:
Thermoplastics: plastics that harden on cooling and can be remelted and reshaped (e.g., PP, PE, PC, PA, and ABS)
Thermosetting plastics: heat-moldable materials that can only be shaped once, so they are not reusable (e.g., epoxy, melamine, and polyurethane)
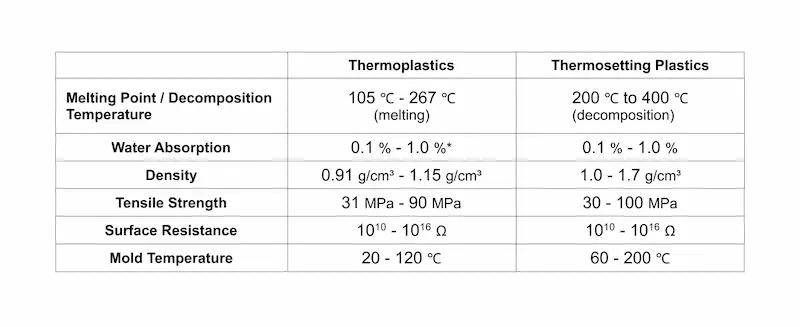
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of their key characteristics (these are wide ranges based on selected materials):
Both thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics are predominantly low to moderate in UV resistance (with some exceptions) and benefit from using additives. Their flammability also varies based on additives, though the chemical structure of thermosetting plastics makes them slightly more flame-resistant.
How to make molded plastic
Once a material is selected, there are numerous ways to process it. Frequently used methods include:
Injection molding: Ideal for mass production of complex, detailed parts, notably consumer electronics, medical devices and toys.
Compression molding: Common for products that need strength and durability, such as household appliances, plastic seals, and automotive parts.
While each process functions best with different types of meltable plastic, they often overlap. For example, moldable plastic pellets are best for injection molding, blow molding and extrusion. On the other hand, clear moldable plastic can be used in all of the above.
Finally, the molds are prepared using metal, silicone or even 3D printing, and materials are fed through. Once cooled, products are removed and ready for use.
Is moldable plastic sustainable?
With so many molded plastic products on the market, it’s natural to wonder about the environmental footprint.
Molded plastics can be made from both biodegradable and non-biodegradable sources. Obviously, those made from renewable resources are compostable, and they use less energy during production, increasing their sustainability.
Additionally, thermoplastics are more easily recycled because they can be remelted and remolded into new products. Unfortunately, since thermosetting plastic can’t be remelted, it has limited options at the end of its lifecycle, and recycling is not at the top of that list.
Shaping the future
Due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility, molded plastics are undoubtedly a critical part of manufacturing across global industries. As environmental factors continue to dominate the plastics industry, the future of molded plastics will continue to evolve.