The Power of 3D Printed Plastics
When it comes to printing plastic, is 3D printing cheaper than molding?
19/08/2025
By Web Editorial Team
2min read
When it comes to printing plastic, is 3D printing cheaper than molding?
19/08/2025
By Web Editorial Team
2min read

When it comes to printing plastic, is 3D printing cheaper than molding?
The short answer: Maybe.
Cost is based on several factors, such as production volume, part complexity, material cost and the type of molding process. However, with its flexibility and ability to create complex geometries, printing plastic has become a popular (and viable) option.
Let’s take a closer look at 3D plastic printing.
There are two types of printers used to print plastic:
Filament printers: More affordable, easier to use and able to print larger volumes
Resin printers offer higher precision and a smoother finish, and resins are available in formulations for specialty projects.
Determining which 3D printer is better, filament or resin, depends on your project needs and applications.
There are over a dozen resins that can be used when printing plastic. Those that stand out for all-purpose printing include:
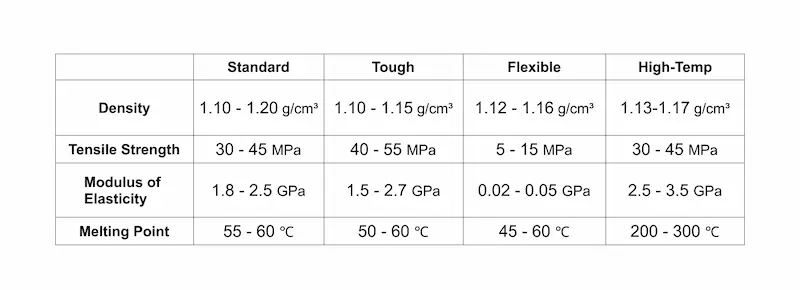
Thanks to their versatility, durability and ease of use, thermoplastics are a staple material for filament-based (FDM) 3D printing. While several types are used (including nylon), Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) stand out. So, what is the difference between PLA and TPU, and what makes them popular?
PLA (Polylactic Acid):
Made from renewable resources, PLA is biodegradable and one of the easiest materials to print. Unfortunately, its low heat resistance (around 60°C) makes it unsuitable for high-temperature environments.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane):
Known for its almost rubber-like flexibility, TPU has excellent abrasion and heat resistance but can be hard to print because of its elasticity.
FDM can print polyethylene (PE), but—much like TPU—PE’s flexibility makes the process difficult. However, with specialized machine settings and temperatures, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) can be printed.
Though both processes create plastic parts, the concept of 3D printing vs. injection molding isn’t entirely accurate. 3D printing is typically used for quick, low-volume production, while injection molding is preferred for mass production.
Rather than pitting the two against each other, it is more accurate to say the processes complement one another. Many companies will use 3D printing to create prototypes and turn to injection molding for high-volume manufacturing to make the final product.
In some cases, injection molding from 3D-printed molds is possible. This approach is a cost-effective way to test mold designs and can quickly handle low-volume production. Unfortunately, 3D-printed molds lack the durability and heat resistance of their metal counterparts.
As 3D printing offers cost-effective and efficient manufacturing solutions, and as technology advances, the possibilities for plastics are endless.
29/01/2026
By Web Editorial Team
2min read
17/01/2026
By Web Editorial Team
1min read
20/12/2025
By Web Editorial Team
2min read
02/12/2025
By Web Editorial Team
2min read
Copyright© 2026 PlaBase. All Rights Reserved.