In today’s world, not a day goes by without using plastic products. Whether it’s your eyeglasses, vehicle headlights or kitchen cookware, we are dependent on the strength of engineered plastics like polycarbonate (PC).
Among the many types of plastics, polycarbonate is renowned for its durability, lightweight, and high impact resistance. Let’s look at what makes PC so versatile.
The history of PC
As early as the 1890s, German chemist Alfred Einhorn experimented with reacting phosgene with bisphenol A (BPA). However, it wasn’t until the mid-1950s that PC was commercially manufactured by Bayer and soon after, other companies worldwide, including General Electric, began production. As advancements in safety equipment, automotive, personal electronics and more increased, so did the use of polycarbonate (PC). However, environmental and health concerns about BPA have grown, leading to increased research on ways to produce non-BPA polycarbonates.
What is PC material?
Polycarbonate (PC) is a family of polymers characterized by carbonate ester linkages in the backbone.
- Phosgene (solvent) method: Reaction of bisphenol A (BPA) with phosgene
- Transesterification (melt) method: Reaction of bisphenol A (BPA) and diphenyl carbonate without phosgene
In short, BPA is converted to its sodium salt and then mixed with a phosgene solution to react. From there, the polymer is separated from any impurities, rinsed, dried and turned into pellets. PC density is higher than that of other common plastics, ranging from 1.20-1.22g/cm³. Additives, like glass fibers and plasticizers, can have a significant impact on not only the density of polycarbonate but also on polycarbonate yield strength.
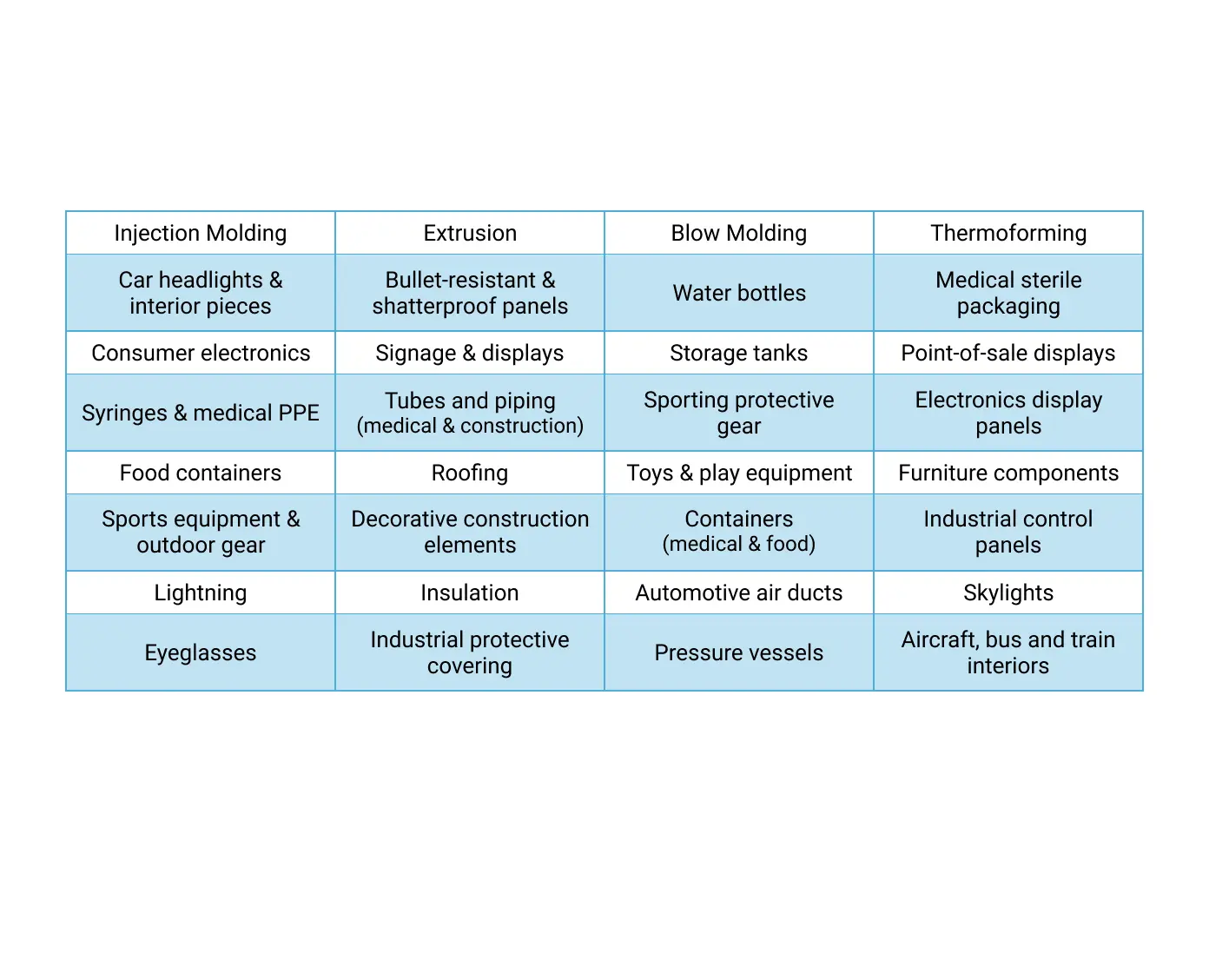
Polycarbonate processing and products
PC pellets are easy to process into a wide range of products using a variety of methods, like:
Polycarbonate texture varies from smooth and glossy to matte, textured, frosted or rough, depending on the processing method chosen. The surface finish of a polycarbonate mold is critical to PC's final texture and look. But no matter how much you use it, PC won't break easily and it has great design potential.
What are the features of PC?
- Resilience: Polycarbonate's chemical resistance includes water, alcohols, organic and inorganic acids and alkalis
- Durability: Withstands wear, pressure and damage
over long periods, even in low temperatures between -30°C and -40°C - Polycarbonate impact resistance: Tolerates force without breaking, cracking or deforming
- Transparency: At a thickness of 2-3mm, the light transmittance is 85-90%, which is roughly equivalent to that of methacrylic resin
- Heat resistance: Stable mechanical properties from −40 °C to 120 °C
- Dimensional stability: There is little change when exposed to high heat or during moisture absorption
- Food hygiene: Minimal leaching makes it compliant with food hygiene standards (Notification No. 20)
Despite PC being one of the most widely used general-purpose engineering plastics, there are some drawbacks. Polycarbonate’s thermal conductivity is low compared to other materials, it is costly; it may become brittle upon UV exposure; and it is susceptible to abrasion. Scratch-resistant polycarbonate is available, but coatings or treatments must be applied.
Polycarbonate FAQs
Q: Does polycarbonate block UV?
A: PC gives some level of UV resistance, but prolonged exposure to UV radiation may result in yellowing, loss of mechanical properties and brittleness.
Q: Is polycarbonate recyclable?
A: Yes, though there are several steps to ensure it is ready for new products.
Q: Is polycarbonate strong?
A: Yes, it is known for its durability and is one of the strongest thermoplastics produced.
Q: Can you laser cut polycarbonate?
A: It is possible, but there are safety concerns; material thickness, potential melting/discoloration, and laser settings must be considered.
Q: What is the melting point of polycarbonate?
A: PC has a fairly high melting point of 267°C(≈513 °F).