Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is a multipurpose, adaptable thermoplastic considered a go-to material for demanding environments. Thanks to its resilience when exposed to heat and chemicals, PPS is used in everything from consumer goods and construction to aeronautics and automotive.
What is polyphenylene sulfide?
The ISO abbreviation for polyphenylene sulfide is PPS. It is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer with a straight-chain structure of alternating bonds between phenyl groups (benzene rings) and sulfur (S). The chemical structure is represented as (-C₆H₄ S-)ₙ. There are three types of PPS polymers: Cross-linked, semi-cross-linked and linear.
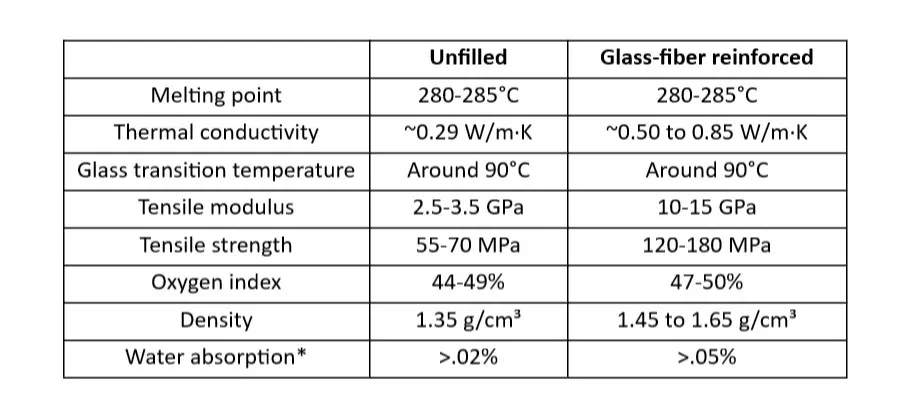
PPS plastic is known for its strength, rigidity and resistance to abrasion, heat and chemicals. However, adding glass fiber or other inorganic fillers (commonly 40wt%) gives it is an increased performance boost. Below we compare the differences between unfilled and reinforced PPS.
*(24-hour immersion)
Additionally, it has an oxygen index of 47, and when exposed to flames, the surface carbonizes, protecting the inside and making it highly flame-retardant.
Despite its popularity, PPS plastic material does have disadvantages, including:
- Poor adhesion: With no oils or solutions able to melt PPS below 200°C and low surface energy, it has difficulty bonding.
- Brittleness: In low temperatures, breaks or cracks can form when subjected to impact or stress.
- Complex processing: Due to elevated processing temperatures, specialized equipment is required for manufacturing.
- High cost: More expensive than similar thermoplastics, limiting where and when it is used.
What is PPS plastic used for?
As industries worldwide look for metal replacement, the demand for polyphenylene sulfide has grown. However, automakers were some of the earliest adopters.
Gasoline-powered vehicles use about 400 to 500 grams of PPS per vehicle, while hybrid vehicles (HVs) use three to four times that number. Just ten years ago, PPS accounted for about 30% of car materials, but today, that number is closer to 50-60%.
PPS's long-term heat and high chemical resistance are ideal for housing electric water pumps and parts around the engine, such as insulators and converters. With the production of HV's on the rise, demand is expected to continue.
PPS material compared to other plastics
Q: What is the difference between PTFE and PPS?
A: Unlike PTFE — a fluoropolymer with a carbon backbone fully bonded with fluorine atoms — PPS does not contain fluorine and is considered a thermoplastic polymer. They have similar chemical and temperature resistance, but PPS demonstrates better mechanical strength.
Q: What is the difference between PP and PPS?
A: PP and PPS are thermoplastics, but PP is made from propylene with a repeating hydrocarbon backbone. Additionally, PP deforms at lower temperatures (over 110°C) than PPS.
Q: What is the difference between PPS and PPA?
A: Like the previous question, PPA and PPS are engineered thermoplastics, but PPA is polyamide (nylon) made from dicarboxylic acids and aliphatic diamines. PPA’s thermal resistance is commonly 120-180°C, making it lower than PPS.
Is PPS plastic biodegradable?
Globally, most plastics are thermoplastics and those which are biodegradable is limited. PPS plastic falls outside of that limited range and is not biodegradable. However, its high chemical and heat resistance (studies have not found an oil or solution that melts PPS below 200°C) means it can withstand harsh environmental factors. Plus, its stable backbone means it will not break down easily. PPS can be recycled and reused when properly managed.
PPS: Robust and reliable
PPS plastic thrives in high-stress, high-temperature environments. And while there are a few limitations, it’s countless benefits make it a highly valuable material across the manufacturing industry.