What do clothing brands like Patagonia and Adidas have in common with automakers like Ford and BMW? They are all leaning into consumer appeals for eco-conscience products, so whether that’s recycled plastic shoes or vehicle dashboards, maximizing the potential of sustainable materials made from plastic is trending worldwide.
What is cotton plastic?
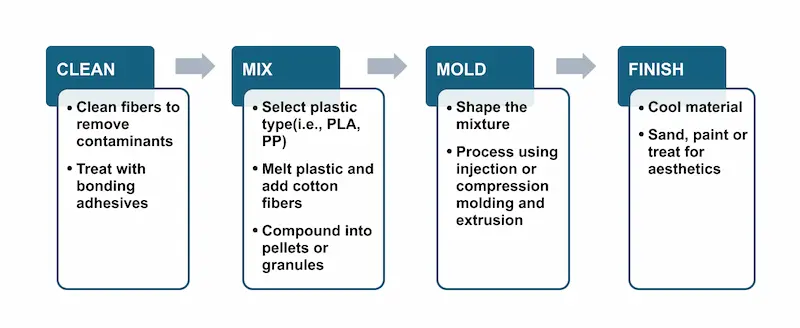
Cotton plastic is a hybrid material that blends natural cotton fibers with melted plastic polymers using the following process:
Adding cotton to plastic materials reinforces the structural strength without a sizable weight increase. Cotton fibers are naturally hollow, meaning they have a low density that takes up more volume without adding mass. Plus, cotton plastic reduces environmental impact by adding renewable, biodegradable components.
Although it may sound like a recycled fabric material for clothing, cotton plastic is not used to produce apparel. Instead, it is typically used to make products like packaging materials, automotive parts and construction items where durability is required.
Recycled plastic clothing
Clothes made from recycled plastic turn waste — usually plastic bottles — into fibers that can be woven or knitted into fabric. But if cotton plastic isn’t used to make garments, how are recycled plastic clothes made? Here’s quick breakdown:
Collection: Plastic bottles are collected from waste sites and sorted by type
Cleaning: Labels, glue, etc., are removed, and bottles are shredded into plastic flakes
Melting: Create plastic liquid then push through small holes to create thin strands
Formation: Plastic strands are spun into yarn the woven or knitted to create fabric
Finishing: Fabric can be dyed or treated to increase texture or softness
Production: Material is cut and sewn into
While recycled nylon can be used for apparel, recycled polyester fabric (rPET) is the most popular clothing material made from repurposed plastic. Used to craft eco clothing like recycled t-shirts, shoes made from plastic bottles and more, rPET has a significant environmental impact. Not only does it prevent plastic waste from hitting landfills, but it also conserves resources, including water and energy, while emitting fewer greenhouse gases. Plus, rPET is quick-drying and durable (like virgin polyester), making it functional and fashionable.
With all this in mind, what is the disadvantage of recycled polyester fabric? Like virgin polyester, when washed, rPET sheds microplastics — tiny particles that are a main contributor to ocean pollution. Additionally, because the fiber quality breaks down over time, there is limited recycling potential, and when it is recycled, it demands significant energy use.
Recycled polyester fabric FAQs
Q: Are recycled clothes safe to wear?
A: Definitely! Recycled clothing is thoroughly cleaned and tested for chemical safety. Several certifications, like the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) and OEKO-TEX, support health and safety standards.
Q: Are recycled clothes good quality?
A: Recycled clothing has incredible potential but depends on the materials, recycling process and brand production standards. In some cases, it can match or exceed the quality and standards of non-recycled garments.
Q: Is recycled polyester better than cotton?
A: One is not better; it’s based on use and purpose. For example, recycled polyester is moisture-wicking, making it an ideal choice for activewear; however, cotton is preferred for its comfort and breathability.
Q: What does recycled polyester feel like?
A: It can be hard to tell the difference between recycled polyester and virgin polyester. It is adaptable, with a smooth surface and slight stretch. It is considered comfortable and, with some finishing treatments, mimics natural fabrics.
Sustainable plastic materials: repurposed and reimagined
Driven by consumers looking for green, eco-friendly products and solutions to environmental waste, sustainable materials made from plastic are critical to the circular economy. Research continues to explore advanced recycling, upcycling and progressive technology to trigger holistic changes.